Germany’s pension policies are at the forefront of a crucial debate that affects millions of citizens. As the nation grapples with the future of pensions, key figures like Steffen Kampeter, Managing Director of the Confederation of German Employers’ Associations, stress the importance of a careful evaluation rather than hasty decisions. This ongoing discourse reflects the broader debate on the welfare state in Germany, highlighting the necessity for thoughtful reform in European pension systems. With 96 percent of wages being granted as pensions in many countries, questions arise about whether Germany can maintain its current structure without risking its welfare state. As stakeholders engage in this discussion, the implications for the nation’s economic stability and citizen well-being are more significant than ever.
The conversation surrounding pension systems in Germany has evolved into a vital topic of discourse reflecting a complex interplay of policy, societal needs, and economic factors. Recent insights have prompted a reconsideration of the current framework, especially in light of comparisons with other welfare systems across Europe that have openly tackled similar challenges. Influential voices, including Steffen Kampeter, advocate for a measured approach when contemplating future adjustments, warning against the potential pitfalls of adhering rigidly to traditional practices. As debates about the sustainability of pensions progress, the need to innovate while respecting the foundation of the welfare state becomes increasingly clear. Hence, the future of retirement security in Germany remains under scrutiny as policymakers explore alternatives that could shape both the economic landscape and citizens’ expectations.
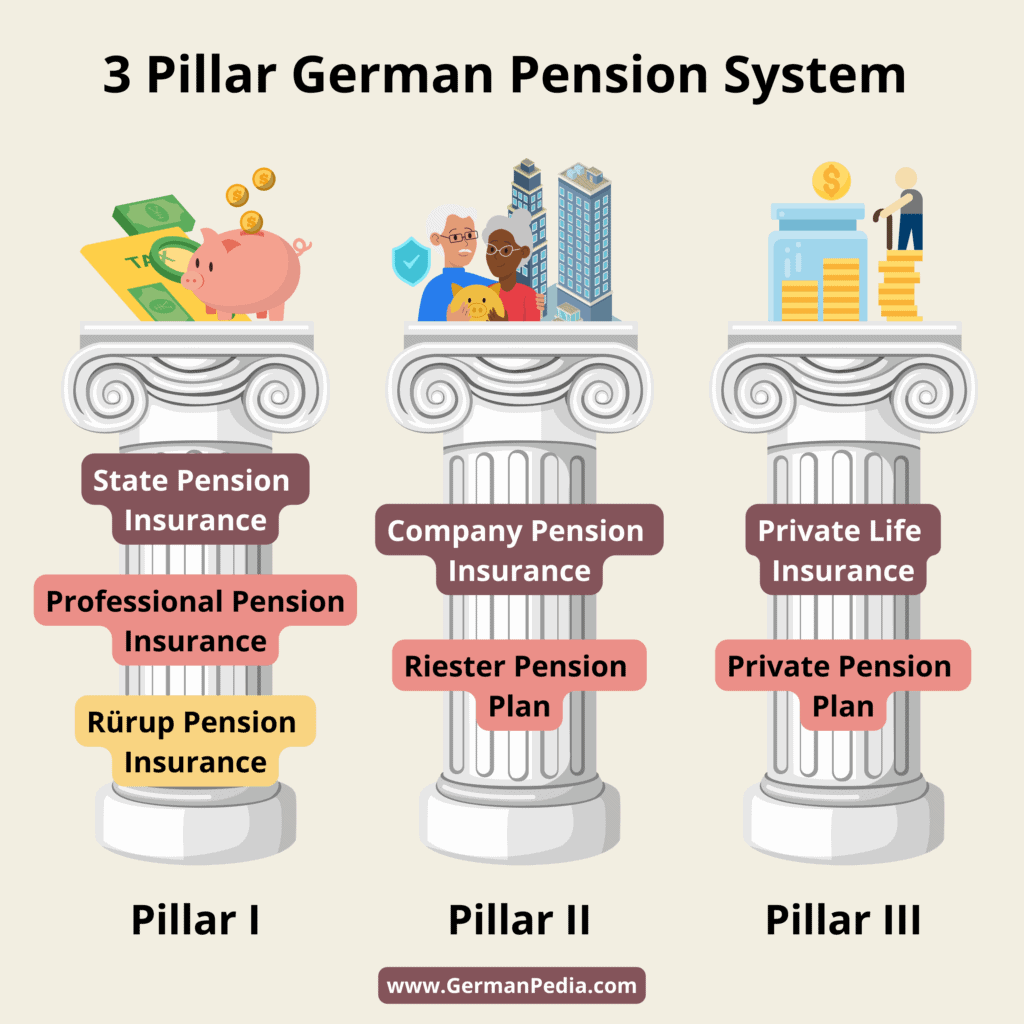
Understanding Germany’s Pension Policies
Germany’s pension policies are a subject of intense scrutiny and ongoing debate, particularly as the nation prepares for the challenges posed by an aging population. There is a growing consensus among policymakers and economists that the existing pension framework may not adequately support the welfare state in the long term. Discussions surrounding the future of pensions have been reignited by voices like Steffen Kampeter, who advocates for a careful reevaluation of existing systems rather than a hasty shift to new ideologies. In shaping Germany’s economic future, understanding these policies is crucial.
The pension debate in Germany reflects wider concerns echoed in other European pension systems. Countries such as Sweden and Denmark have established innovative models that focus on sustainability and adequacy of pensions for all ages. By studying these examples, Germany can delve into effective reforms that prioritize the security of its citizens while also maintaining the viability of the state welfare system. Such an analysis enhances the dialogue on what future reformations Germany might needs to undertake.
The Future of Pensions in Germany
The future of pensions in Germany has become increasingly uncertain, with many advocating for a rethink of traditional approaches. As demographics shift and the workforce ages, the financial sustainability of the current pension system is at risk. Stakeholders, including Steffen Kampeter, argue that without proactive measures, Germany could face a crisis that threatens to undermine the welfare state. As such, future pension policies should not only address immediate financial needs but also anticipate longer-term societal changes.
The pension debate is not just a German phenomenon; it’s part of a broader European context where different countries are addressing similar challenges. As policymakers gather data and insights, it’s essential to consider successful strategies employed elsewhere. By examining how other European pension systems have adapted to changing demographic realities, Germany can craft a robust pension strategy that shields its citizens while ensuring that the welfare state remains intact.
Lessons from European Pension Systems
The examination of various European pension systems unveils insightful lessons for Germany. For instance, many countries within Europe allocate a higher percentage of wages towards pensions than Germany, which traditionally relies more on state-supported frameworks. This discrepancy presents an opportunity for Germany to explore innovative pension solutions that blend social security with private savings, thereby promoting long-term stability and resilience in its welfare model.
Moreover, understanding the dynamics of pensions across Europe shines a light on the emerging need for multigenerational support systems. Such frameworks not only provide financial backing to retirees but also engage younger generations in proactive savings and investment strategies. By looking at successful European models, Germany can embark on reforming its pension policies to create a more equitable and sustainable future for all citizens.
Challenges Facing the German Welfare State
The welfare state in Germany is currently facing numerous challenges, exacerbated by shifts in demographics and economic pressures. Steffen Kampeter’s cautionary perspective on the urgency of pension reform resonates with many citizens who fear that rash changes might result in a diminished social safety net. The ongoing discourse points to the necessity for a balanced approach that prioritizes both fiscal responsibility and citizen welfare.
In particular, the demographic shift towards an aging population means that fewer workers are supporting a larger retiree group, threatening the sustainability of the welfare system. This demographic reality is reflected across other European nations, which have had to rethink their own pension systems. As Germany engages in this global conversation about welfare and pensions, it must consider solutions that prioritize long-term sustainability while ensuring adequate support for its aging citizens.
Debating the Future of German Pensions
The debate surrounding the future of pensions in Germany is more than just a fiscal discussion; it’s intertwined with the societal values of equity and social responsibility. Figures like Steffen Kampeter play a key role in shaping this discourse, urging stakeholders to engage thoughtfully rather than reactively. The urgent need to address these issues reflects concerns about the adequacy of pensions for future retirees, given the existing economic frameworks.
Furthermore, as the pensions debate intensifies, stakeholders must also consider the influence of external factors such as globalization and technological advancements. The conversation about pensions is also a grassroots one, calling for active participation from the populace who are directly affected by these policies. By fostering an inclusive dialogue, Germany can better prepare its welfare system for the complexities of tomorrow’s economic landscape.
The Role of Stakeholders in Pension Policy
Stakeholders ranging from government officials to financial experts and everyday citizens play a crucial role in shaping pension policy in Germany. Influencers like Steffen Kampeter are pushing for a collaborative approach that transcends political posturing, aiming instead for solutions that will impart long-term benefits for all demographics. Engaging these varied perspectives is essential in navigating the complexities of pension reform to ensure fairness and viability of the welfare state.
Moreover, stakeholder involvement typically leads to richer discussions and more innovative approaches to pension policies. By integrating insights from various sectors, Germany can analyze the effectiveness of existing pension systems and consider ideas that have successfully bolstered pensions in other European contexts. Achieving a broad consensus on necessary reforms will fortify the reliability of the pension system while also reenforcing public trust in the welfare state.
Reforming Germany’s Pension System
Reforming Germany’s pension system requires a multifaceted approach that considers not just financial sustainability but also social equity. The impact of decisions made today echoes into the future, prompting discussions led by figures like Steffen Kampeter to advocate for cautious yet decisive reforms. A thoughtful reevaluation of existing policies could lead to a more responsive and adaptive pension landscape, better suited to the needs of current and future generations.
Countries that have succeeded in reforming their pension systems often share common traits: flexibility, inclusivity, and foresight. Germany could draw from these lessons, designing a pension model that balances security for the elderly with growth opportunities for the economically active population. As the pension debate unfolds, the aim should be to cultivate a system that reflects the values of the welfare state while ensuring adequate support for all citizens.
The Importance of Public Awareness in Pension Reforms
Public awareness is paramount in the ongoing discussion about pension reforms in Germany. Citizens need to be informed about the implications of current policies and the potential changes that may arise. Steffen Kampeter and other thought leaders stress that the conversation shouldn’t be confined to policymakers alone; it must also include an engaged public that understands the rationale behind proposed reforms and their potential impact on the welfare state.
Fostering public discourse enhances transparency and trust in the processes driving pension reforms. When the population is well-informed, it is better equipped to participate in the debate and advocate for solutions that align with their interests and needs. As Germany moves forward, embracing an open dialogue with its citizens will be fundamental in securing a future-proof pension system that respects both current contributions and future obligations.
Ensuring Sustainable Future Pensions
The ultimate goal of the ongoing discussions about pensions in Germany is to ensure sustainable future pensions. As evolutionary shifts in demographics shape the landscape, policymakers like Steffen Kampeter emphasize proactive measures over reactive adaptations. This forward-thinking approach is vital in designing a pension system that not only supports retirees but is also rooted in fiscal responsibility and social solidarity.
To achieve sustainability, Germany must explore innovative financing strategies that blend public support with private initiatives. As seen in other European pension systems, a diversified portfolio can lead to enhanced stability and resilience. By integrating successful concepts from international models, Germany can cultivate a robust pension strategy that balances benefits across generations and secures the welfare state for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main issues in the current pension debate in Germany?
The current pension debate in Germany highlights concerns about the sustainability and adequacy of the pension system. Key issues include the need for reform to address demographic changes, the financial viability of pensions, and the potential impact on the welfare state. Discussions led by figures like Steffen Kampeter emphasize the importance of careful consideration before implementing reforms, cautioning against rushing into decisions that could jeopardize the welfare system.
How is the future of pensions being addressed in Germany?
In addressing the future of pensions in Germany, policymakers are exploring reforms that balance sustainability with the needs of retirees. Input from experts like Steffen Kampeter suggests that while urgent changes may not be necessary, it is vital to engage in thoughtful discussions about pension contributions and benefits. The future design of pensions aims to ensure stability while adapting to changing demographics and economic conditions.
What lessons can Germany learn from other European pension systems?
Germany can learn valuable lessons from European pension systems, particularly regarding the equitable distribution of pension benefits. In many European countries, employees receive a higher percentage of wages as pensions compared to Germany’s system. This comparative perspective highlights the need for a reflective approach to ensure that the German pension system remains competitive and sustainable within the wider European context.
What role does the welfare state play in the discussion of Germany’s pension policies?
The welfare state is central to the discussion of Germany’s pension policies, as the pension system is a key component of social security. Policymakers like Steffen Kampeter stress that maintaining a robust welfare state requires re-evaluating current pension frameworks. The ongoing discourse reflects a commitment to protecting the welfare state while ensuring pensions are financially viable and equitable for future generations.
How does Steffen Kampeter influence the pension debate in Germany?
Steffen Kampeter, as the Managing Director of the Confederation of German Employers’ Associations (BDA), influences the pension debate in Germany by advocating for a cautious approach to reforms. He emphasizes the need for thorough reflection on current policies to prevent jeopardizing the welfare state. His insights encourage a balanced dialogue on the future of pensions, considering both economic factors and social equity.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Germany’s current pension system is a controversial topic. |
| Steffen Kampeter, BDA Managing Director, advises against rushing decisions for 2031 pensions. |
| It’s important to reflect thoughtfully on future pension policies rather than cling to old systems. |
| Kampeter warns that sticking to the current pension situation risks undermining the welfare state. |
| Comparison with other European countries shows 96% of wages are granted as pensions elsewhere. |
| The future design of the welfare state in Germany needs careful consideration and debate. |
Summary
Germany pension policies are currently under scrutiny as discussions intensify about the future of the country’s pension system. The ongoing dialogue emphasizes the necessity for thoughtful evaluation of existing practices. Experts like Steffen Kampeter have highlighted potential risks in maintaining the status quo, warning that it could jeopardize the nation’s welfare state. As comparisons are drawn with other European systems, it becomes evident that Germany may need to rethink its approach to pensions to ensure stability and sustainability going forward.