The EU Climate Service has revealed alarming data: 2025 was the third warmest year on record globally, surpassed only by 2023 and 2024. This significant rise in temperatures underscores the urgent issues linked to global warming and the pervasive effects of greenhouse gases in our atmosphere. Researchers from the European Climate Service Copernicus have highlighted this concerning trend, emphasizing the profound implications for European climate policy and our planet’s future. As we witness increasingly extreme weather patterns and a concerning climate change report, the reality becomes clear—our actions today are defining the climate of tomorrow. Looking ahead, the projections indicate that 2025’s data is merely a prelude to the escalating challenges we will face if substantial action isn’t taken to mitigate these changes.
The European Climate Service has been pivotal in assessing recent atmospheric trends, revealing that the past few years have seen unprecedented warmth across the continent. This comprehensive evaluation highlights critical developments in climate science, linking every increase in temperature to anthropogenic factors, primarily the increase in greenhouse gas emissions. As we move forward in our understanding of climate dynamics, the implications for policy-making and environmental management become ever more vital. The latest findings indicate that not only are we experiencing global warming, but its manifestations are intricately tied to Europe’s climate policies and international commitments. Addressing these issues through effective strategies can significantly influence our collective response to the ongoing climate crisis.
2025: A Milestone Year in Global Warming
The year 2025 marks an unsettling milestone in the ongoing narrative of global warming. It has become the third warmest year recorded globally, with pivotal contributions from the years 2023 and 2024 which set the stage for this increase. This worrying trend is underscored by data released by the EU Climate Service, which highlights that these temperature spikes are not merely anomalies but part of a long-term trajectory linked to human activity and greenhouse gas emissions. As scientists continue to analyze climate change reports, it’s evident that the implications for ecosystems and human societies are becoming increasingly dire.
Global warming is intricately tied to the accumulation of greenhouse gases, which have peaked significantly in the last decade. Factors contributing to this rise include continued reliance on fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas for energy and transportation. Each contribution is exacerbating climate conditions, with 2025’s data solidifying the notion that we are facing a climate crisis that demands urgent response and action. Not only are temperatures rising, but the frequency and severity of extreme weather events are becoming commonplace, leading to devastating impacts on populations and the environment.
EU Climate Service’s Role in Monitoring Climate Change
The EU Climate Service, particularly through its Copernicus program, plays a crucial role in tracking and reporting climate changes across Europe and the globe. Their recent findings indicate that Europe is experiencing the fastest warming rate of any continent, with 2025’s average of 10.4 degrees Celsius highlighting this alarming trend. As a premier source of data, the EU Climate Service provides insights that are vital for shaping European climate policy and public awareness regarding the effects of climate change. Having access to accurate and timely information empowers nations to formulate comprehensive strategies aimed at reducing emissions and mitigating climate-related impacts.
Through extensive climate change reports, the EU Climate Service has repeatedly demonstrated how the effects of greenhouse gases, particularly carbon dioxide, are escalating. The agency’s findings are not just statistics; they are a call to action for policymakers and citizens alike. As projected, the increase in temperature will lead to severe weather patterns, such as floods and droughts, unless concrete actions are taken to curb these emissions. The task now falls on governments to respond adequately to the insights provided by the EU Climate Service to avert the looming climate crisis.
The Rising Tide: Effects of Greenhouse Gases
Greenhouse gases are the primary culprit behind global warming, leading to significant shifts in climate patterns worldwide. In 2025, the accumulation of these gases remained alarmingly high, primarily due to human activities such as industrial processes, transportation emissions, and deforestation. The relationship between these emissions and the increasing frequency of extreme weather events cannot be overstated. Rising temperatures have been linked to a multitude of negative impacts, including more hot days, severe storms, and heightened health risks for vulnerable populations.
The implications of unchecked greenhouse gas emissions extend beyond immediate climatic changes. As evidenced by the COPERNICUS reports, nations worldwide are witnessing a surge in climate-related health issues, exemplified by increased heat-related fatalities. The European climate policy framework aims to address these challenges by proposing significant reductions in carbon emissions. However, achieving these ambitious targets requires not just governmental commitment but an engaged public willing to support sustainable practices and lifestyle changes.
The Forecast Beyond 2025: European Climate Policy Challenges
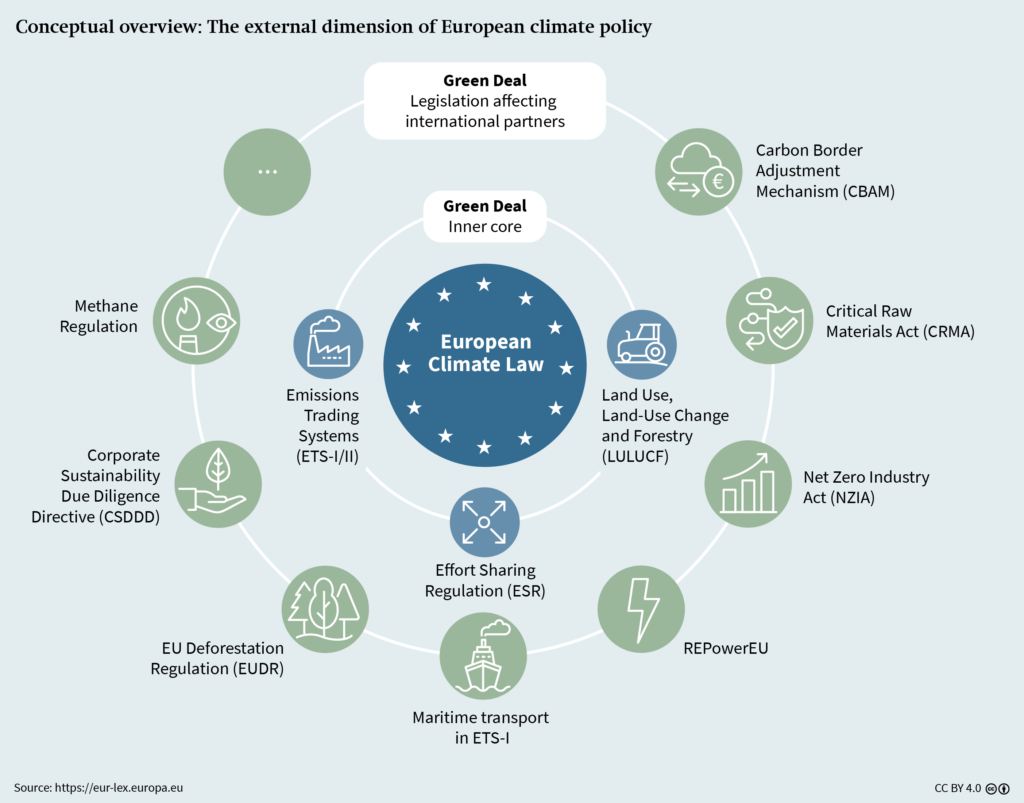
Looking forward, European climate policy faces significant challenges ahead of the goals set by the Paris Climate Agreement. With the scientific consensus moving toward an acknowledgment that the threshold of 1.5 degrees Celsius will soon be surpassed, urgent legislative action is needed to curb emissions. The EU Climate Service’s assessments illustrate not just the rate of change but also pave the way for necessary policy adjustments by revealing gaps in current regulations. As outlined in recent communications, achieving a 55% reduction in CO2 emissions by 2030 is a critical target that requires vigorous efforts across sectors.
A crucial aspect of successfully navigating the climate policy landscape is dealing with political pressures that may ebb the momentum needed for robust legislation. Recent hesitancies around significant EU climate bills—such as those addressing deforestation and emissions trading—highlight the complexities of enacting necessary reforms. To combat climate change effectively, a coordinated and forward-looking approach is paramount, ensuring that innovations and initiatives keep pace with the increasingly alarming climate data being reported.
Extreme Weather and Health Risks
The year 2025 saw a staggering rise in extreme weather incidents, further highlighting the urgent need for heightened climate action. The effects of these events are far-reaching, impacting not only the environment but also public health. Weather-related disasters have resulted in increasing challenges, with heatwaves being particularly hazardous; the World Health Organization has identified them as a leading cause of climate-related deaths. As global temperatures rise, regions that experience prolonged periods of extreme heat are likely to see exacerbated health crises and increased mortality rates.
Such trends necessitate that energy and climate policies prioritize public health as part of their core strategies. The European climate policy framework must consider comprehensive approaches to safeguard vulnerable populations from extreme weather health risks. By integrating public health perspectives into environmental policy, nations can better prepare for the inevitable impacts of climate change—escalating the importance of sustainable developments across industries to protect current and future generations.
Global Responses to Climate Data
The global community’s response to rising temperatures and climate data released by agencies like the EU Climate Service is crucially important. The frequency of extreme weather events, as detailed in the climate change report for 2025, calls for enhanced international cooperation and commitment to climate action plans. As world leaders convene at various summits, the urgency for collaboration in tackling climate change remains a focal point. Sharing best practices and climate data not only fosters transparency but also ensures that all countries can benefit from proven strategies that mitigate the effects of climate change.
Furthermore, engaging in global dialogue about the impacts of greenhouse gases emphasizes the importance of collective action. Nations must reinforce their commitments to reducing emissions while actively investing in renewable energy resources to combat climate change more effectively. By fostering a collaborative culture around climate governance, countries can develop innovative solutions to tackle what has become one of humanity’s greatest challenges—ensuring that future generations inherit a healthier, more sustainable planet.
Understanding the Connection: Climate Change and Economy
The interplay between climate change and economic stability cannot be overlooked as we assess the repercussions of events like those reported for 2025. As temperatures rise and extreme weather becomes more common, economies may face unprecedented stress, particularly in sectors reliant on natural resources. The effects of greenhouse gases not only affect environmental sustainability but also impose heavy financial burdens on governments and communities globally. Industries tied to agriculture, insurance, and infrastructure are particularly vulnerable, highlighting a clear need for resilient economic strategies that take climate change into consideration.
As we navigate through these economic implications, it’s vital to prioritize investment in sustainable technologies and infrastructure that promote a green economy. By adopting policies that encourage eco-friendly practices, governments can stimulate job creation while simultaneously addressing climate concerns. The interplay between climate resilience and economic viability will dictate how effectively nations meet their climate goals and mitigate the impacts of global warming.
Future Projections and It’s Impact on Biodiversity
The consequences of climate change extend well beyond human society, affecting ecosystems and biodiversity significantly. With global warming projected to continue, as seen with the data from 2025, the strain on wildlife habitats and natural resources is likely to intensify. Ecosystems in Europe, particularly, are at a critical juncture, facing the dual pressures of rising temperatures and habitat loss due to anthropogenic factors. As each year reveals alarming statistics, the urgency to implement robust conservation policies becomes increasingly clear.
Proactively addressing climate change is pivotal to protecting biodiversity and maintaining ecosystem integrity. The EU Climate Service has been instrumental in shedding light on these issues, providing essential data to inform conservation strategies. Collaboration across countries, coupled with long-term commitments to protecting natural spaces and biodiversity-rich regions, can foster resilience against climate change impacts, ultimately supporting a myriad of species that contribute to the planet’s health.
Public Awareness and Climate Action
Raising public awareness about climate change and the resultant effects is paramount in fostering a culture of action and responsibility. The reports detailing the third warmest year, alongside increased extreme weather incidence, serve as a wake-up call to citizens worldwide. Empowering individuals to understand the implications of global warming and greenhouse gas emissions can instigate changes at the grassroots level, driving demand for better practices in energy conservation, waste management, and sustainable consumption.
Moreover, engaging the community in climate initiatives helps build resilience against future eco-challenges. Grassroots movements and advocacy play a crucial role in complementing governmental actions, pushing for necessary reforms and encouraging the adoption of sustainable technologies. Collective action at all levels—individual, local, and global—will be instrumental in addressing the multifaceted climate crisis we continue to face.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the implications of the EU Climate Service’s report on global warming for 2025?
The EU Climate Service has reported that 2025 was the third warmest year on record globally. This highlights the continued trend of increasing global temperatures, driven primarily by greenhouse gases. These high temperatures are associated with extreme weather events, emphasizing the urgent need for effective climate change strategies.
How does the EU Climate Service contribute to understanding climate change reports?
The EU Climate Service provides vital data and assessments on climate change, including temperature records and the effects of greenhouse gases. By documenting trends like the record warmth observed in 2025, it helps policymakers and the public grasp the gravity of climate change and informs European climate policy.
What is the relationship between greenhouse gases and the extreme weather events reported by the EU Climate Service?
The EU Climate Service attributes the rise in extreme weather events to the increasing levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. As 2025 showed record warmth, the resultant droughts, wildfires, and floods underscore how these gases impact weather patterns and climate stability.
Why is 2025 considered one of the warmest years, according to the EU Climate Service data?
According to the EU Climate Service, 2025 was the third warmest year recorded due to a combination of factors including the continuous increase in greenhouse gas emissions from various human activities, demonstrating a clear link to climate change.
What trajectory is Europe on concerning climate policy in light of the EU Climate Service findings?
Despite reduced greenhouse gas emissions by 37% since 1990, the EU Climate Service suggests that Europe must enhance its climate policies to meet the Paris Agreement’s goal of a 55% reduction by 2030. Current pressures and setbacks in EU climate legislation highlight the challenges faced in this trajectory.
How does the EU Climate Service track the impacts of climate change across Europe?
The EU Climate Service monitors temperature trends, reports on greenhouse gas levels, and evaluates extreme weather impacts across Europe. Their assessments, including the sobering data from 2025, provide insights into how climate change is affecting regional climates and public health.
What does the EU Climate Service predict for the future climate in Europe?
The EU Climate Service suggests that Europe is experiencing an alarming trend of increasing temperatures and will likely face more severe weather events, which underscores the critical need for robust climate policies and action to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| 2025 Temperature Record | 2025 was recorded as the third warmest year globally since record-keeping began, closely following 2023 and 2024. |
| Impact on Europe | Europe is experiencing the fastest warming, with an average temperature of 10.4°C in 2025. |
| Polar Regions | The Arctic and Antarctica recorded significant temperature highs, highlighting alarming warming trends. |
| Greenhouse Gas Emissions | The increase in greenhouse gases from industrial activities is contributing to rising temperatures. |
| Extreme Weather | 2025 saw 157 extreme weather events, including droughts and heatwaves, driven by human activities. |
| WHO Findings | Heat is a significant cause of weather-related fatalities, with half of the global land area facing extreme heat days. |
| EU Climate Goals | The EU aims for a 55% reduction in emissions by 2030, but political pressures threaten this progress. |
Summary
The EU Climate Service reports that 2025 marked a pivotal year in the ongoing climate crisis, capturing attention as the third warmest year in recorded history. This unprecedented heat underscores the urgent need for robust climate action to mitigate further temperature increases and their associated impacts on health and environmental stability.