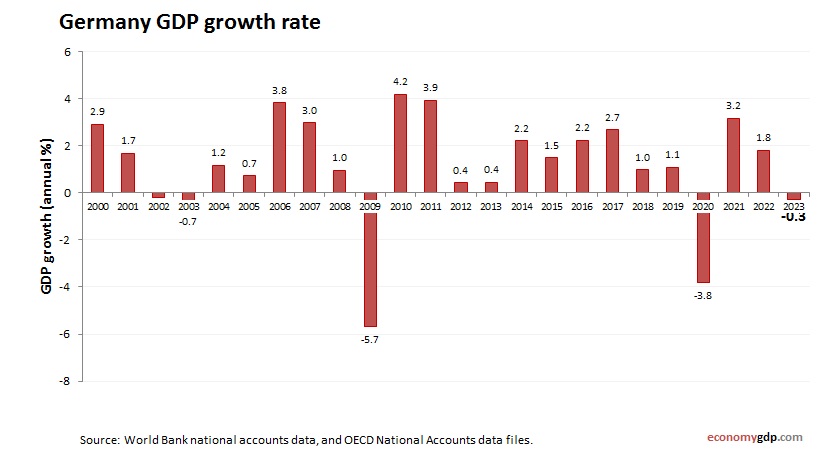
Germany’s economic growth is a pivotal element of the European landscape, especially as we look toward the future. As we step into 2026, there is cautious optimism surrounding the German economy, primarily driven by a robust economic stimulus package aimed at invigorating growth. However, the current climate reflects mixed signals; despite government efforts, challenges like the ongoing decline in industrial production and lower GDP forecasts persist. Experts are focused on not just immediate outcomes but also the long-term health of the workforce, particularly in traditional sectors hit hard by recent job cuts. As debate swirls over the future of the German economy, it is crucial to balance short-term fixes with comprehensive reforms to maintain a competitive edge in the global market.
The prospects for growth in Germany’s economic landscape are under intense scrutiny as we approach 2026. Observers are closely watching the nation’s recovery trajectory, especially in light of recent downturns in industrial performance and the looming specter of inflation. The government’s substantial financial stimulus, aimed at revitalizing key sectors, illustrates a commitment to stimulate economic activity. Nevertheless, sectors such as manufacturing remain vulnerable, reflecting a broader concern for the nation’s economic health. As discussions shift to the sustainability of these efforts, industry leaders emphasize the importance of innovation and adaptability in securing a prosperous future for the German economy.
Germany’s Economic Growth Prospects for 2026
As we look ahead to 2026, Germany’s economic growth is a significant topic of discussion among economists and industry leaders. The recent government’s stimulus package, which totals 500 billion euros, aims to rejuvenate the economy by investing in vital sectors such as infrastructure and defense. This infusion of funds is expected to play a crucial role in reversing the current trend of economic decline, where industrial production has faced a downturn for four consecutive years. Analysts, like Jörg Krämer from Commerzbank, believe that an effective use of this financial support could lead to higher growth rates; however, it raises the question of whether these efforts will be sustained or simply viewed as a temporary measure.
Moreover, despite the optimism from government initiatives, challenges persist. The ifo Institute’s forecast for a mere 0.8% increase in GDP for 2026 reflects widespread concerns about the structural issues plaguing the German economy. Factors such as declining exports, especially to key markets like the USA, and stagnant industrial performance throw a shadow over potential recovery. Additionally, many small and medium-sized enterprises remain skeptical about the government’s ability to implement necessary reforms alongside the stimulus measures. The complexity of addressing these long-standing issues suggests that while there may be prospects for growth, significant hurdles must be overcome.
The Impact of Economic Stimulus in Germany
The introduction of a substantial economic stimulus plan serves as a beacon of hope for Germany’s lagging industries. This 500 billion euro package not only symbolizes the government’s commitment to fostering economic recovery but is also geared towards addressing systemic issues that have hindered progress. Investment in infrastructure is particularly crucial, as it promises not only immediate job creation but also long-term benefits by enhancing productivity across various sectors. The anticipation surrounding tax cuts and the reduction of bureaucratic obstacles highlights a collective effort to create a more conducive environment for business growth.
However, the implementation of such a vast stimulus plan without accompanying reforms could lead to fleeting benefits. Critics, including economic experts like Ulrich Kater, emphasize the need for a comprehensive approach that includes restructuring policies along with financial input. This dual strategy could ensure that the measures taken do more than just provide a temporary uplift in economic figures, but rather result in sustained improvements to Germany’s economic fabric. Without addressing underlying issues such as the structural decline in industrial production, the efforts may resemble not more than a short-lived boost in growth.
Challenges in the German Industrial Sector
The latest reports on the German economy indicate that the industrial sector is undergoing critical challenges, particularly with a marked decline in production over recent years. Industries such as automotive and machinery construction have been severely impacted, leading to significant job losses and growing disappointment among workers and employers alike. Peter Leibinger, president of the Federation of German Industries, notes that this decline is not merely cyclical but indicative of deeper structural issues that must be confronted to facilitate recovery.
Economic observers also point out that Germany’s reliance on traditional industries may be a limiting factor in terms of future growth. The rapid pace of global competition, particularly from countries like China, demands innovation and adaptability. Volker Treier, head of foreign trade at the German Chamber of Commerce, highlights that the competitiveness of German export markets has been waning. A pivot towards embracing digitalization and new technologies like Artificial Intelligence could prove crucial for revitalizing industrial capabilities and regaining market share on the global stage.
GDP Forecasts and Economic Realities
The forecasts for Germany’s GDP in 2026 paint a sobering picture amidst government hopes for recovery. With predictions of just a 1% increase by the Kiel Institute for the World Economy, there is palpable concern that the economy is not positioned for a robust recovery. Such modest expectations reflect the global economic environment’s impact on Germany, where sluggish demand and competitive pressures are stifling growth. Analysts warn that these forecasts could worsen if no concrete measures are taken to stimulate both domestic and international demand.
Moreover, the economic forecasts signify an urgent need for policy reform to foster resilience in the face of such challenges. The underlying issues affecting the economy, including the long-standing reliance on exports and traditional industries, call for innovative approaches that cater to evolving market dynamics. Although short-term boosts in growth may be realized through stimulus measures, achieving sustainable, long-term economic health necessitates significant structural changes.
Future of the German Economy: Opportunities and Innovations
Looking ahead, the future of the German economy could hinge on its ability to adapt and embrace innovation. With the digital transformation underway, there lies an opportunity for companies to rethink traditional business models and leverage technology to improve efficiency and productivity. Experts argue that by harnessing advancements in areas such as Artificial Intelligence, Germany can unlock new avenues of growth, especially in sectors that have historically struggled against international competition.
Moreover, the transition to sustainable practices in industries may also play a pivotal role in shaping the future landscape of the German economy. As global attention increasingly focuses on climate change and sustainability, German industries are positioned uniquely to lead in green technology and renewable energy sectors. By investing in sustainable solutions while maintaining economic stability, Germany has the potential to not only recover from its current challenges but to emerge as a leader in future economic paradigms.
Addressing the Skills Gap in German Industry
One of the persistent challenges that German industries face is a significant skills gap among the workforce. As technology evolves, particularly with an increased focus on digital competencies and automation, many workers find themselves unable to keep pace. This mismatch creates difficulties for businesses looking to innovate and remain competitive. Investing in education and training programs tailored to future industry needs is essential to safeguard Germany’s economic interests.
To bridge this skills gap, collaboration between educational institutions, government agencies, and businesses is critical. Initiatives that promote lifelong learning and vocational training can empower workers to adapt to new technologies and methodologies. By cultivating a workforce that is well-equipped for the challenges of tomorrow, Germany can not only improve its economic standing but also enhance the overall resilience of its industries. This proactive approach could turn the current challenges into opportunities for growth and innovation.
Reforming Economic Policies for Sustainable Growth
For Germany to rebound effectively from its current economic state, comprehensive reforms to economic policies are imperative. Many experts advocate for a departure from traditional approaches in favor of more dynamic, flexible strategies that can be quickly adjusted based on results. Such policies should focus not only on immediate financial relief but also on ensuring long-term structural improvements that promote innovation and competitiveness.
Policymakers should consider incorporating feedback mechanisms that allow industries to voice their challenges and contribute solutions. Lessons learned from international models, particularly from fast-paced economies like the United States, can inform Germany’s policy-making process. Emphasizing pragmatism over perfectionism could foster a landscape where experimentation and adaptation are welcomed, ultimately leading to a more resilient and dynamic economy.
Encouraging Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) play a crucial role in the German economy, making up a significant portion of employment and economic output. However, recent economic challenges have disproportionately affected these businesses, leaving many feeling uncertain about their future. Financial constraints and declining consumer demand have placed a strain on SMEs, which often lack the resources to weather economic downturns effectively. Policies aimed at supporting these enterprises are essential in nurturing the backbone of the German economy.
Proposed initiatives that focus on access to financing, innovation incentives, and reducing regulatory burdens could help revitalize SMEs. Additionally, creating networking opportunities and collaborative platforms can enhance their ability to compete in the global market. By prioritizing the needs of these businesses, Germany can foster a more robust economic landscape that is better equipped to navigate future challenges while driving sustainable growth.
Navigating Global Economic Challenges
Germany’s economic outlook does not occur in isolation; it is deeply intertwined with global trends and challenges. Recent tensions in international trade, particularly with major partners such as the United States and China, have created an unpredictable economic environment. Changes in international policy and trade agreements can significantly influence Germany’s economic performance and should be closely monitored. It is crucial for German businesses to understand global market dynamics to adapt effectively and maintain their competitive edge.
In response to these global challenges, Germany must consider crafting policies that not only bolster domestic growth but also enhance international competitiveness. Collaboration with other nations, focusing on trade diversification, and supporting innovation in export-oriented sectors can position Germany favorably on the international stage. A proactive approach that anticipates global shifts will be vital in ensuring that the German economy can navigate these challenges while capitalizing on new opportunities for growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current state of Germany’s economic growth in 2026?
As of January 2026, Germany is experiencing a challenging economic landscape, with modest growth prospects. The GDP is expected to rise by only 0.8%, significantly lower than earlier predictions. Despite a government stimulus package of 500 billion euros aimed at infrastructure and tax cuts, many believe that comprehensive reforms are necessary to ensure sustained economic growth in Germany.
How does the government stimulus package impact Germany’s economic growth?
The 500 billion euro stimulus package is designed to boost economic growth in Germany by investing in infrastructure and defense, as well as implementing tax cuts. While it is expected to generate some growth, experts caution that without simultaneous reforms, the effectiveness of this stimulus in creating long-term economic growth may be limited.
What are the challenges facing the future of the German economy?
The future of the German economy faces several challenges, including a decline in industrial production for four consecutive years, disappointing export performance, particularly to the USA, and ongoing difficulties for small and medium-sized enterprises. These factors contribute to a cautious outlook for Germany’s economic growth.
What is the forecast for Germany’s GDP growth in 2026?
Current forecasts predict that Germany’s GDP growth will reach a mere 0.8% in 2026. This is a downward revision from earlier estimates, reflecting concerns about structural issues within the German economy and the lack of significant recovery indicators.
How is the decline in industrial production affecting the German economy?
The prolonged decline in industrial production is significantly impacting the German economy, especially traditional sectors such as automotive and machinery. This has led to job cuts and growing frustration among businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises, affecting overall economic sentiment.
What role does digitalization play in the future of the German economy?
Digitalization is expected to play a crucial role in the future of the German economy by transforming work processes and creating new business opportunities. As industries adapt to new technologies, there is potential for renewed economic growth, provided the necessary reforms and investments are made.
Why are SMEs important for Germany’s economic growth?
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are vital for Germany’s economic growth as they comprise a significant portion of the employment landscape and contribute to innovation. However, they are currently facing challenges such as declining exports and increased competition, which could hinder their role in driving future economic growth.
What implications does the economic situation have for employment in Germany?
The current economic situation, characterized by a decline in industrial production and a sluggish growth forecast, has negatively impacted employment, particularly in traditional sectors. Job cuts are becoming more common, affecting the overall labor market and potentially leading to higher unemployment rates.
What is the sentiment among economists regarding Germany’s economic recovery?
Economists express a mix of cautious optimism and concern regarding Germany’s economic recovery. While there are hopes for growth driven by government stimulus, many analysts warn that without addressing underlying structural issues, any economic upturn may be short-lived.
How can the German economy improve beyond 2026?
To improve beyond 2026, the German economy may need to embrace pragmatic approaches to policy-making, invest in innovation, and enhance competitiveness. Strategies such as embracing digitalization, reducing bureaucratic hurdles, and fostering a culture of experimentation could help Germany regain its economic momentum.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Economic Upturn Expectations | Germany is hoping for economic growth in 2026 supported by a stimulus package. |
| Challenges | Continued declines in industrial production, especially in traditional industries like automotive and chemical sectors. |
| Economic Forecasts | Growth predictions have been downgraded, with the GDP expected to rise only by 0.8% to 1% in 2026. |
| Government Stimulus Package | A 500 billion euro package aimed at infrastructure and tax cuts, but concerns over lack of comprehensive reforms persist. |
| Digitalization and AI Potential | Increased digitalization and AI adoption are expected to open new business opportunities. |
| Need for Pragmatic Approach | Economists advocate for a less perfectionistic, more experimental policy approach. |
| Competitive Landscape | Germany needs to develop new strategies in the face of global competition and political uncertainties. |
Summary
Germany’s economic growth hinges on a combination of government stimulus and structural reforms. With the 500 billion euro package aimed at boosting infrastructure and other sectors, hopes are high for an upturn in 2026. However, there are significant challenges such as declining industrial production and weakened export performance that need to be addressed. Moving forward, embracing digitalization and strategic adaptability will be crucial for revitalizing the German economy.