China’s economy is currently navigating a period of significant transition and challenge. Despite a remarkable export boom contributing to a massive trade surplus of $1.2 trillion in 2025, the nation’s GDP growth has alarmingly slowed, reaching its lowest level since the end of strict COVID restrictions nearly three years ago. The latest figures reveal an annual growth rate of 5.0 percent, just meeting the government’s target, yet it marks one of the weakest performances in decades. Central to this slowdown is waning domestic demand, exacerbated by a beleaguered real estate market and a tightening labor market, which are stifling consumer spending. As economists watch closely, the dual challenges of stimulating internal growth while capitalizing on its robust export capabilities remain pivotal for China’s future economic trajectory.
The economic landscape of China reflects a complex interplay of various factors influencing its growth dynamics. As the world’s second-largest economy grapples with unprecedented challenges, interest centers around its gross domestic product trends and the implications of a seemingly resilient export sector. While the significant trade surplus continues to highlight China’s capacity to engage global markets, domestic consumption has faltered under the weight of declining real estate investments and labor market strains. Investors and analysts are keenly observing how these fluctuations will shape consumer behavior and overall economic activity moving forward. Understanding China’s economic narrative requires a nuanced approach to the interplay between international trade and internal market forces.
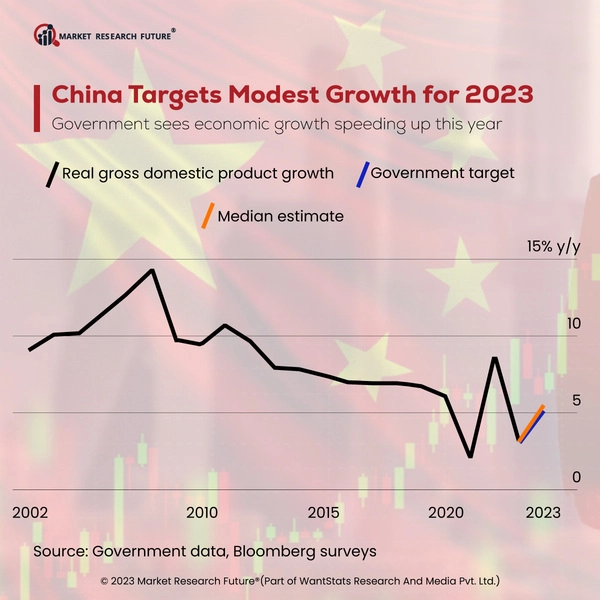
Overview of China’s Economic Growth in 2025
In 2025, China’s economy showcased a surprising trend despite the impressive export boom that has defined its recent growth. The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) increased by only 4.5 percent in the fourth quarter of the year, representing the slowest growth rate in over three years. This stark figure underscores a critical shift as the economy transitions from dependency on exports to more sustainable factors. Experts are concerned that the challenges posed by weak domestic demand, particularly in sectors such as real estate, have raised alarms about the continued health of the Chinese economy.
Throughout the year, China’s annual growth rate was reported at 5.0 percent, aligning precisely with the government’s target. However, the significance of this achievement is diminished when placed in the context of decades of robust growth. Analysts are attributing this low growth figure primarily to deteriorating domestic conditions, exacerbated by a sluggish labor market and declining real estate prices. The increase of only 0.9 percent year-over-year in retail sales during December exemplifies the consumer reluctance stemming from these economic pressures.
Impact of Domestic Demand on China’s Economic Outlook
The weakening of domestic demand is becoming a critical concern for policymakers in China. With consumer spending dampened and investments plummeting, particularly in the real estate market, the overall economic resilience of the country is severely tested. The drop in investment in fixed assets by 3.8 percent highlights the lack of confidence among domestic investors. Coupled with the 17.2 percent decline in real estate investments, the government’s plans to stimulate domestic consumption face significant hurdles.
As retail sales continue to stagnate, a key player in China’s economic health, it raises questions about future growth. Experts argue that the sustained period of minimal domestic consumption has direct implications for the nation’s GDP growth trajectory, leading to lower forecasts for future economic performance. Organizations such as the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund offer gloomy predictions, projecting growth rates around 4.4 and 4.5 percent for the upcoming year. This trend raises alarms about China’s ability to maintain its economic status without robust domestic demand.
China’s Export Boom amidst Economic Slowdown
Despite the slow domestic recovery, China’s export sector remains a prominent pillar sustaining its economic framework. The year 2025 saw a record trade surplus of $1.2 trillion, highlighting the resilience of exports even in the face of adverse trade relations, particularly with the United States. Although exports to the U.S. faced a significant decline of approximately 20 percent due to heightened trade tensions, China’s economy found refuge in diversifying its export markets to mitigate losses. Other regions expressed strong demand for Chinese goods, compensating for the downturn in trans-Pacific trade.
The sustaining nature of exports amid a slowing economy illustrates the importance of international trade for China’s current and future economic landscape. While the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund provide forecasts of reduced growth, they simultaneously recognize that robust exports could be pivotal in avoiding more severe economic contractions. As the dynamics of global trade evolve, ensuring a balanced relationship with diverse partners will be critical for China to navigate its economic challenges successfully.
Challenges in the Real Estate Market
The real estate market, a long-standing engine of growth in China’s economy, is currently facing unprecedented challenges. The decline of 17.2 percent in real estate investments last year is indicative of broader investor anxiety stemming from falling property values and regulatory crackdowns. As home prices decrease, consumer confidence falters, leading to a vicious cycle that further dampens economic performance. This contraction poses a significant risk as the real estate sector plays a vital role in driving employment and consumption within the domestic market.
Moreover, the struggles of the real estate sector send ripples through other industries, illustrating the interconnectedness of the economy. Declining construction activities and related services consequently hurt fixed asset investments, further constraining potential growth. As the government grapples with stabilizing this critical sector, it remains imperative that comprehensive policies are developed to support real estate recovery and instill confidence back among consumers and investors.
Future Projections for China’s Economy
Looking ahead, the projections for China’s economy appear cautiously optimistic, albeit fraught with uncertainty. Analysts are suggesting growth rates of approximately 4.4 to 4.8 percent for the upcoming years, reflecting a modest recovery trajectory. However, pressing factors such as demographic decline and the need for restructuring the economy towards greater domestic consumption will challenge these forecasts. The demographic shift, marked by a population decrease of 3.39 million in 2025, underscores the urgency for policies aimed at revitalizing consumer spending and investment.
The interplay between exports and domestic factors will dictate the future health of China’s economy. As foreign markets remain a critical lifeline capable of sustaining economic stability, simultaneously enhancing domestic demand is essential. Upcoming years will necessitate innovative policy measures from the Chinese government to harness opportunities for growth while addressing structural weaknesses. The balancing act between external and internal economic pressures will be paramount as China navigates its pathway in the global economy.
The Role of Trade Surplus in Economic Stability
China’s remarkable trade surplus serves as a stability anchor in turbulent economic times, particularly evident in 2025 with a surplus reaching $1.2 trillion. This surplus indicates a strong export performance, especially in a global market replete with uncertainties. The trade surplus not only injects much-needed capital into the economy but also reflects China’s competitive advantage in manufacturing and production capabilities, enabling it to weather domestic challenges.
Ultimately, the trade surplus mitigates the impact of contracting domestic demand and investment declines. However, reliance on exports introduces vulnerabilities, especially as global trade dynamics shift. Continuous engagement with diverse international markets and seeking trade diversification can enhance China’s economic resilience. Policymakers must harness the trade surplus effectively to stimulate domestic consumption and bolster overall economic performance.
Demographic Trends Affecting China’s Economic Growth
China’s recent demographic changes, particularly a declining population, present a formidable challenge for its economic growth ambitions. The country witnessed a population decrease of 3.39 million in 2025, a continuing trend that raises significant concerns around labor availability and consumer spending prospects. With the workforce aging and shrinking, the consumption base is bound to feel the brunt of the decline, impacting everything from retail sales to investment levels.
In the context of economic strategies, these demographic trends necessitate urgent government intervention to bolster consumer confidence and spending. Policymakers must address the implications of a shrinking labor force to ensure that social security systems remain sustainable, particularly as pension funds face mounting pressure. As China’s population dynamics shift, innovative approaches will be vital to revitalize both the workforce and domestic demand, ultimately ensuring resilient economic growth.
Investment Trends and Economic Repercussions
Investment trends in China have shown signs of distress, with fixed asset investments declining by 3.8 percent in 2025. This downturn is particularly pronounced in the real estate market, where a staggering 17.2 percent decrease is indicative of broader economic uncertainties. The declining investment landscape raises alarm over future economic potential, as vigorous capital inflows into key sectors are essential for maintaining China’s growth trajectory.
As the Chinese economy faces these investment challenges, it becomes increasingly important to restore investor confidence and facilitate conditions for stability. Effective government policies that promote investments can help revitalize economic growth by encouraging capital flows into productive sectors. Additionally, aligning investments with sustainable development goals will ensure that the recovery taps into the burgeoning demand for innovation and infrastructure development.
Navigating International Trade Relationships
Navigating international trade relationships is critical for China’s economic future, especially given the backdrop of a trade surplus and recent tensions with major partners like the United States. The trade dispute highlighted the fragility of relying heavily on specific markets; however, it also accelerated efforts to explore and secure alternative trading relationships globally. This pivot is essential for maintaining a diverse export portfolio and mitigating risks from geopolitical tensions.
To strengthen international trade ties, China must engage in dialogues that promote mutual economic interests and alleviate trade friction. Seeking cooperation and aligning trade practices with global partners will not only bolster export figures but also enhance overall economic stability. As China looks toward the future, it’s imperative to cultivate robust international relationships that can withstand market volatility.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current state of China’s GDP growth in relation to its economy?
China’s GDP growth in the fourth quarter of 2025 reached 4.5 percent, marking its slowest pace since the end of strict COVID lockdowns. This slowdown highlights significant challenges facing China’s economy, with domestic demand being particularly weak despite a continuing export boom.
How does China’s export boom affect its economy?
Despite a notable export boom contributing to a record trade surplus of $1.2 trillion in 2025, China’s economy is experiencing slower growth due to weak domestic demand. This juxtaposition illustrates how exports remain a crucial pillar of support amidst broader economic challenges.
What factors are impacting China’s domestic demand?
China’s domestic demand is impacted by a strained labor market and falling real estate prices, which dampen consumer spending. With retail sales in December increasing by only 0.9 percent year-over-year, this reflects the struggles within China’s economy to boost internal consumption.
How is the state of China’s real estate market affecting its economy?
The real estate market has seen a significant decline, with investments decreasing by 17.2 percent in 2025. This fall contributes to the overall slowdown in China’s economy, as weaker real estate performance limits confidence and spending in other sectors.
What does China’s trade surplus mean for its economic outlook?
China’s record trade surplus of $1.2 trillion in 2025 demonstrates the strength of its export sector, which remains vital for the economy. However, the ongoing trade tensions and a 20 percent drop in exports to the U.S. suggest challenges ahead, maintaining a nuanced economic outlook for China.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Economic Slowdown | China’s economy grew at only 4.5% in Q4 2025, the slowest pace in three years. |
| GDP Growth for 2025 | China met its GDP growth target of around 5%, but this is one of the lowest rates in decades. |
| Weak Domestic Demand | Factors like a strained labor market and falling real estate prices caused low consumer spending. |
| Investment Decline | Fixed asset investments fell by 3.8%, with real estate down 17.2%. |
| Strong Foreign Trade | Despite challenges, foreign trade supported the economy with a record trade surplus of $1.2 trillion. |
| Future Growth Predictions | Projected growth of around 4.4% to 4.8% in the coming years. |
| Demographic Challenges | China’s population decreased by 3.39 million in 2025, complicating consumption plans. |
Summary
China’s economy faces significant challenges despite registering a record trade surplus and meeting growth targets. Currently, the economy is growing at its slowest rate in years, highlighting issues with domestic demand and investments. As demographic trends further strain the economy, it becomes increasingly crucial for policymakers to adapt strategies to boost consumer spending and sustain economic stability.